The Future of Smart Cities Around the World
The Future of Smart Cities Around the World
Introduction
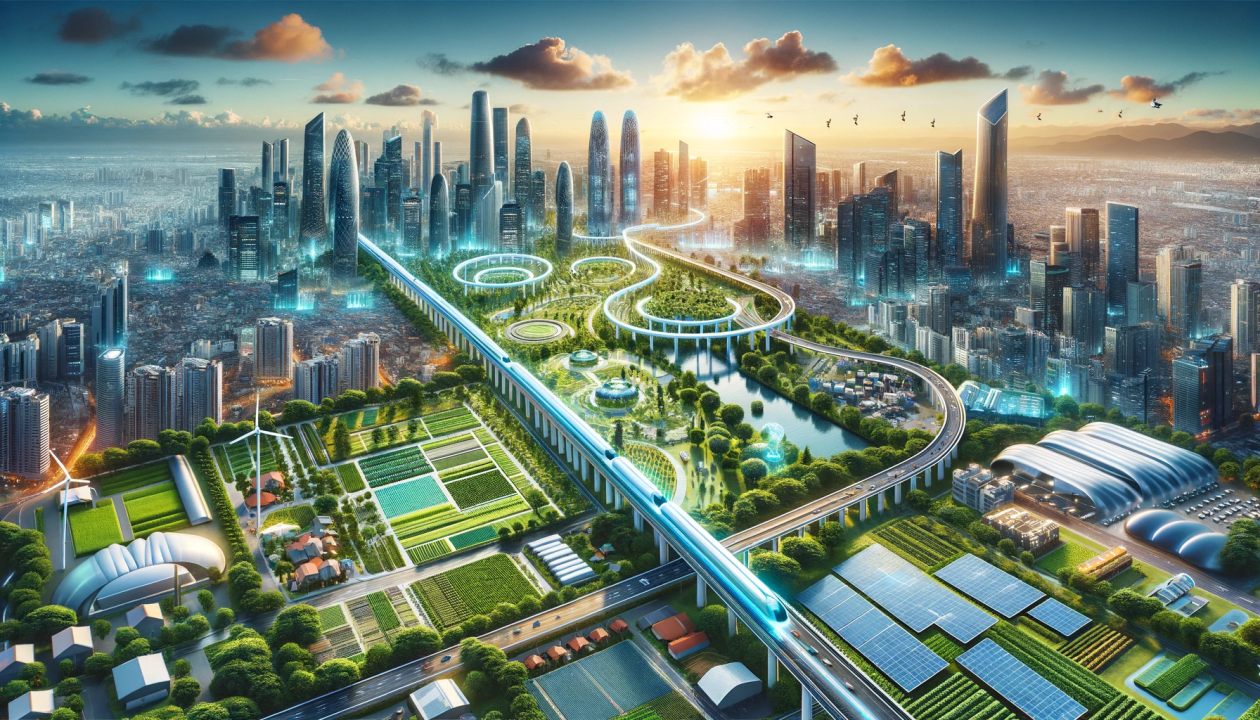
Imagine a city where traffic flows smoothly, energy is used efficiently, and public services are seamlessly integrated. This is the vision of a smart city—a place where technology and data are used to improve the quality of life for residents while promoting sustainability. As the world becomes more urbanized, the concept of smart cities is gaining momentum. This article explores the future of smart cities around the world, the technologies driving this transformation, and the challenges that lie ahead. By understanding the potential of smart cities, we can better prepare for a future that is both innovative and sustainable.
What Are Smart Cities?
Defining Smart Cities
A smart city is an urban area that uses technology and data to enhance the efficiency of services, reduce costs, and improve the quality of life for its residents. These cities leverage the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data to create a connected and intelligent urban environment.
Key Features of Smart Cities
- Smart Infrastructure: Buildings, roads, and utilities are equipped with sensors and connected to a central system for real-time monitoring and management.
- Efficient Transportation: Smart traffic systems, public transit, and ride-sharing services reduce congestion and pollution.
- Sustainable Energy: Renewable energy sources, smart grids, and energy-efficient buildings help reduce the city’s carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Public Services: Smart healthcare, education, and waste management systems improve the quality of life for residents.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Cities use data analytics to make informed decisions and optimize resources.
The Technologies Driving Smart Cities
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is the backbone of smart cities. It involves connecting everyday objects—like streetlights, traffic signals, and waste bins—to the internet. These connected devices collect and share data, enabling real-time monitoring and control.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI plays a crucial role in analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices. It helps cities predict traffic patterns, optimize energy usage, and even detect potential security threats.
Big Data and Analytics
Big data refers to the massive volumes of information collected from various sources. Analytics tools process this data to provide insights that help city officials make informed decisions.
5G Connectivity
5G networks provide the high-speed, low-latency connectivity needed to support the vast number of devices in a smart city. This technology enables real-time communication and data transfer, essential for applications like autonomous vehicles and remote healthcare.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent ways to manage data and transactions. In smart cities, it can be used for everything from secure voting systems to efficient energy trading.
The Benefits of Smart Cities
Improved Quality of Life
Smart cities aim to enhance the quality of life for residents by providing better services, reducing pollution, and improving safety. For example, smart healthcare systems can offer remote consultations, while smart lighting can improve public safety.
Environmental Sustainability
By optimizing resource use and reducing waste, smart cities contribute to environmental sustainability. Smart grids, for instance, can balance energy supply and demand, reducing the need for fossil fuels.
Economic Growth
Smart cities attract investment and create jobs, driving economic growth. The development of new technologies and infrastructure opens up opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs.
Efficient Resource Management
Smart cities use data to optimize the use of resources like water, energy, and transportation. This leads to cost savings and more efficient service delivery.
Examples of Smart Cities Around the World
Singapore
Singapore is often cited as a leading example of a smart city. The city-state uses IoT sensors and data analytics to manage traffic, monitor environmental conditions, and optimize public services. Its Smart Nation initiative aims to harness technology to improve the lives of its citizens.
Barcelona, Spain
Barcelona has implemented various smart city initiatives, including smart street lighting, waste management, and parking systems. The city’s use of IoT and data analytics has significantly improved urban living.
Dubai, UAE
Dubai is working towards becoming a fully smart city by 2021. The city has introduced smart transportation systems, blockchain-based government services, and AI-powered police stations.
Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen is focused on sustainability and aims to become carbon-neutral by 2025. The city uses smart grids, energy-efficient buildings, and data analytics to achieve its environmental goals.
The Challenges of Building Smart Cities
High Costs
Developing the infrastructure for a smart city requires significant investment. This includes the cost of installing sensors, building data centers, and developing software systems.
Data Privacy and Security
The vast amounts of data collected in smart cities raise concerns about privacy and security. Ensuring that data is protected from cyberattacks and misuse is a major challenge.
Technological Integration
Integrating various technologies and systems into a cohesive smart city framework can be complex. Ensuring compatibility and seamless operation requires careful planning and coordination.
Public Acceptance
For smart cities to succeed, they need the support of their residents. Educating the public about the benefits and addressing concerns about privacy and security are essential for gaining acceptance.
Regulatory Hurdles
Building smart cities often involves navigating complex regulations and policies. Governments need to create a supportive regulatory environment to facilitate the development of smart cities.
The Future of Smart Cities
Continued Innovation
The future of smart cities will be driven by continued innovation in technology. Advances in AI, IoT, and 5G will enable even more sophisticated and efficient urban systems.
Increased Collaboration
The development of smart cities requires collaboration between governments, businesses, and citizens. Public-private partnerships will play a crucial role in driving innovation and investment.
Focus on Sustainability
As the world grapples with climate change, sustainability will remain a key focus for smart cities. Future developments will prioritize renewable energy, waste reduction, and green infrastructure.
Global Expansion
The concept of smart cities is gaining traction worldwide. As more cities adopt smart technologies, we can expect to see a global network of interconnected smart cities, sharing data and best practices.
Personalized Services
Future smart cities will offer more personalized services, tailored to the needs of individual residents. This could include customized healthcare, education, and transportation options.
Conclusion
The future of smart cities is bright, with the potential to transform urban living in ways we can only begin to imagine. By leveraging technology and data, smart cities can improve the quality of life for residents, promote sustainability, and drive economic growth. While challenges remain, the continued innovation and collaboration among stakeholders will pave the way for a smarter, more connected world. As we look to the future, the vision of smart cities offers a promising path towards a more sustainable and prosperous urban future.



Post Comment